How to Choose Between Die Casting and Injection Molding for Your Housing Component?
When it comes to manufacturing high-quality housing components—whether for electronics, automotive parts, or industrial equipment—choosing the right production process is a make-or-break decision. Two of the most widely used methods for housing components are die casting and injection molding, but each excels in specific scenarios. As a leading Shenzhen-based 工贸 (industry-trade integrated) foreign trade company with over 8 years of expertise, Shenzhen Sunmy Hardware Co.,Ltd. (visit us at sunmyhardware.com) has helped hundreds of global clients navigate this choice. With our full-suite production capabilities—including Casting, Lathe, Machining, Stamping, and Injection Molding—and strong R&D team, we’ve refined a framework to help you select the optimal process for your housing needs.
1. First: Understand the Core Difference Between Die Casting and Injection Molding
Before diving into selection criteria, let’s clarify the fundamental distinction between the two processes—this will eliminate confusion as you evaluate your project:
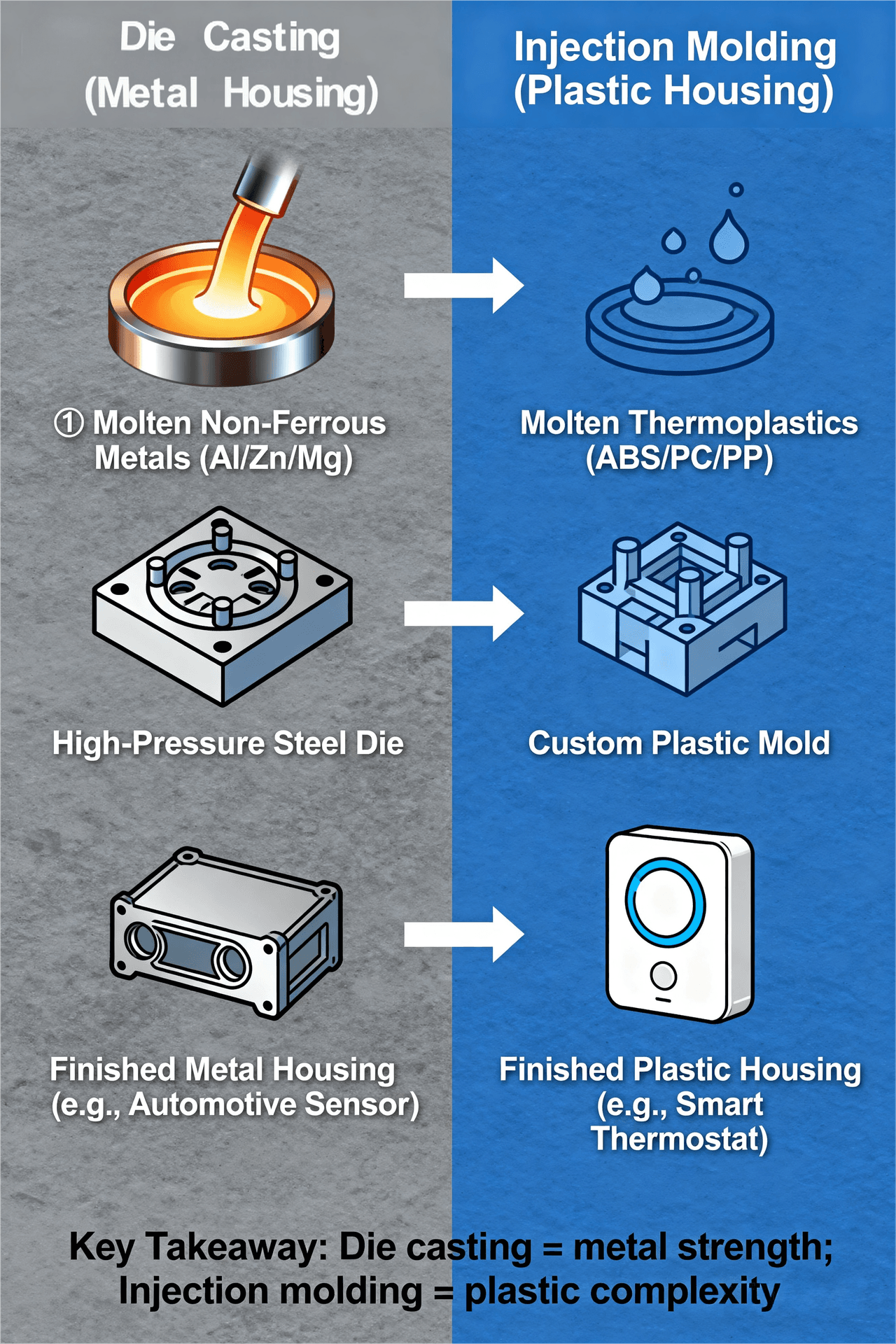
- Die Casting: A metal-forming process where molten non-ferrous metals (e.g., aluminum, zinc, magnesium) are forced under high pressure into a steel mold (called a “die”). Once cooled, the metal part is ejected, ready for finishing (e.g., polishing, coating). It’s ideal for high-strength, heat-resistant housing components.
- Injection Molding: A plastic-forming process where molten thermoplastics (e.g., ABS, PC, PP) are injected at high pressure into a custom mold. After cooling and solidification, the plastic part is removed. It’s favored for complex shapes, lightweight designs, and cost-effective high-volume production.
2. Key Criteria to Guide Your Choice
At Sunmy Hardware, we tailor our recommendations to your project’s unique requirements. Below are the 5 critical factors we use to help clients decide between die casting and injection molding for housing components:
A. Material Requirements: Metal vs. Plastic
The first question to ask is: Does your housing component need to be metal or plastic? This often narrows down your options immediately:
- Choose Die Casting if:
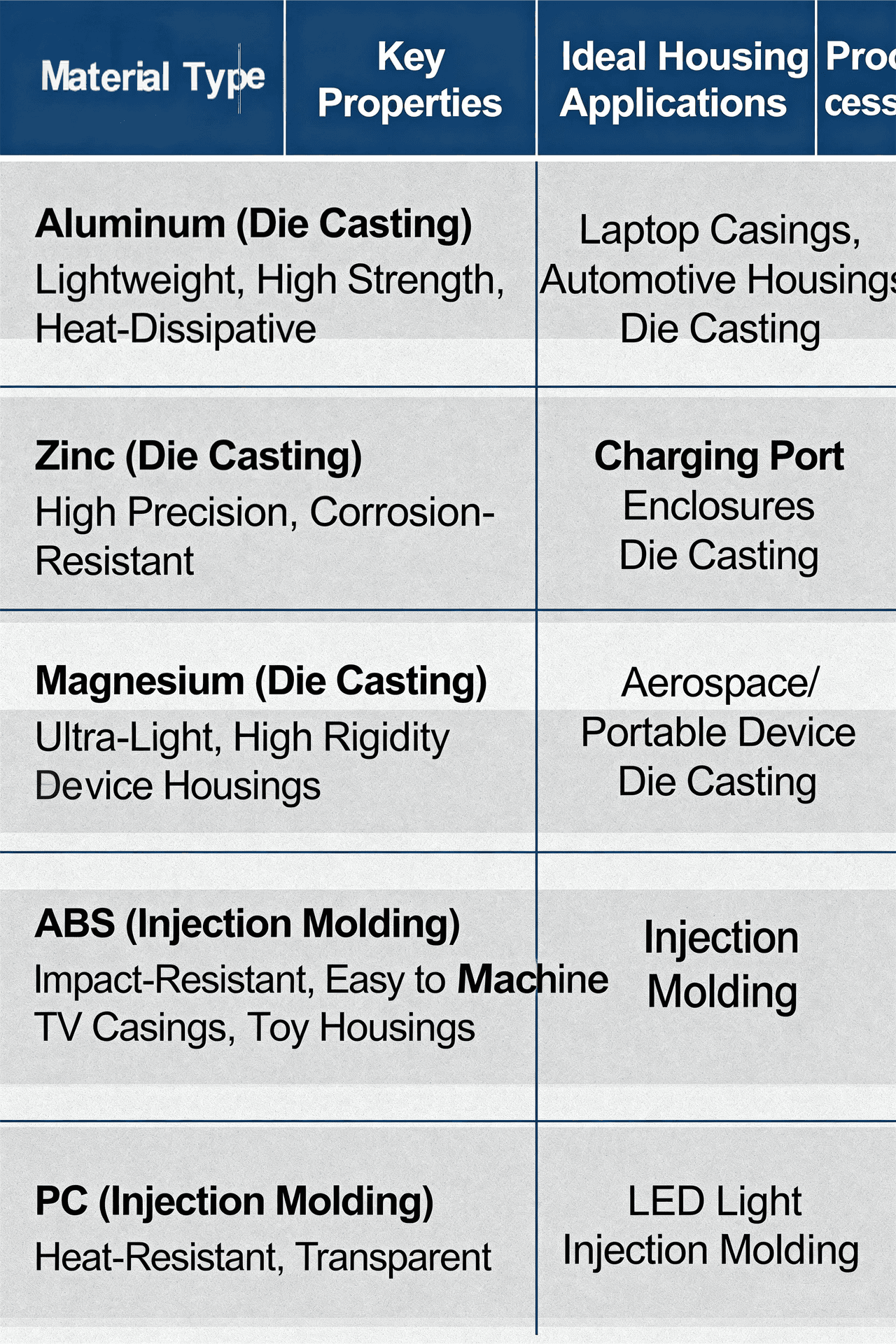
Your housing needs high structural strength (e.g., to withstand impacts or heavy loads), excellent heat dissipation (critical for electronics like LED drivers or automotive engine parts), or corrosion resistance (e.g., outdoor equipment). Common die-cast metals for housings include: - Aluminum: Lightweight, strong, and cost-effective—perfect for consumer electronics (e.g., laptop casings) or automotive housings.
- Zinc: High precision and excellent for small, intricate housings (e.g., smartphone charging port enclosures).
- Magnesium: The lightest die-cast metal, ideal for aerospace or portable device housings where weight is a priority.
Choose Injection Molding if:
Your housing prioritizes lightweight design, complex geometries (e.g., internal ribs, snap-fits, or threaded holes), or flexibility (e.g., soft-touch grips for tools). Plastics also offer superior insulation (great for electrical housings) and a wide range of color/finish options (no need for post-production painting). Popular injection-molded plastics for housings include:
- ABS: Impact-resistant and easy to machine—used in TV casings or toy housings.
- PC (Polycarbonate): Heat-resistant and transparent—ideal for LED light housings or safety goggles.
- PP (Polypropylene): Chemical-resistant—suited for medical device housings or outdoor gear.
B. Production Volume: Low, Medium, or High?
Both processes have different cost structures, so production volume plays a major role in affordability:
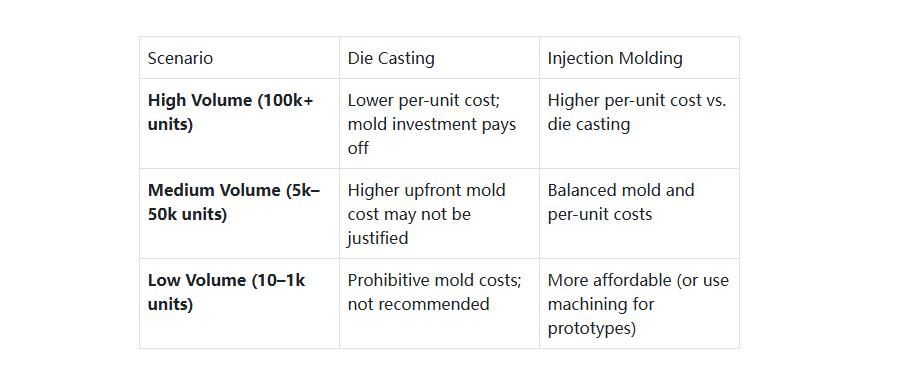
Die Casting: The initial cost of creating steel dies is higher (due to the metal mold’s complexity and durability). However, die casting excels at high-volume production (10,000+ units). Once the die is made, per-unit costs drop significantly—making it cost-effective for long runs (e.g., mass-produced automotive sensor housings).
Injection Molding: Mold costs are lower than die casting (especially for simple designs), and it’s efficient for medium-to-high volumes (5,000+ units). For low-volume projects (e.g., prototype housings or custom medical devices), injection molding is often more budget-friendly than die casting, as the lower mold cost offsets higher per-unit plastic costs.
Pro Tip from Sunmy: If you need a small batch of prototype housings (10–100 units) to test design feasibility, our machining capabilities can bridge the gap—we can create custom metal or plastic prototypes before scaling to die casting or injection molding.
C. Design Complexity: Simple vs. Intricate
The complexity of your housing’s design will also influence your choice:
Die Casting: Best for simple-to-moderately complex shapes with uniform wall thickness (3–5mm is optimal). While modern die-casting technology can handle some intricate details (e.g., thin walls or small holes), it’s limited by the metal’s flow properties—too many undercuts or sharp angles may cause defects (e.g., air bubbles or incomplete filling).
Injection Molding: The clear winner for highly complex designs. Plastics flow more easily than molten metal, so injection molds can accommodate undercuts, internal cavities, thin walls (as low as 0.5mm), and even integrated features (e.g., hinges or gaskets). This reduces the need for post-production assembly—saving time and cost. For example, we recently helped a client design a one-piece plastic housing for a smart thermostat that included built-in wire channels and snap-fits, eliminating 3 separate assembly steps.
D. Cost: Upfront Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
Cost is always a priority, but it’s important to look beyond just per-unit prices—consider upfront mold costs and total lifecycle expenses:
At Sunmy Hardware, we offer transparent cost quotes tailored to your volume. For example, if you need 20,000 aluminum housings for industrial sensors, die casting may be more cost-effective in the long run. If you need 5,000 plastic housings for a new consumer gadget, injection molding will likely save you money upfront.
E. Lead Time: How Fast Do You Need Your Housings?
Lead time is critical for meeting product launch deadlines. Here’s how the two processes compare:
- Die Casting: Mold production takes longer (4–8 weeks) because steel dies require precision machining and heat treatment to withstand high temperatures and pressure. Once the die is ready, production runs are fast (1–2 weeks for 10k units).
- Injection Molding: Mold production is faster (2–4 weeks) for standard plastic molds (though complex molds may take longer). Production runs are also quick—we can deliver 10k plastic housings in 1–2 weeks once the mold is approved.
Sunmy Advantage: Our in-house mold design and production team (no outsourcing!) speeds up lead times by 20–30% compared to competitors. Whether you need die-cast metal or injection-molded plastic housings, we can align with your launch timeline.
3. When to Partner with a Custom Manufacturing Expert Like Sunmy Hardware
Choosing between die casting and injection molding isn’t always black and white. For example:
- What if you need a housing that’s metal for strength but has plastic inserts for insulation?
- What if your design is complex, but you need high-volume production at a low cost?
This is where Sunmy Hardware’s expertise shines. As a 工贸一体 (industry-trade integrated) company, we don’t just manufacture—we collaborate with you to optimize your design for cost, performance, and scalability. Our capabilities include:
- Custom Mold Design: We create dies and molds tailored to your 2D/3D drawings or physical samples (send us your design today at [email protected]).
- Hybrid Solutions: We combine processes (e.g., die casting + injection molding inserts) to meet unique needs.
- End-to-End Service: From prototyping and production to finishing (painting, anodizing, plating) and quality control, we handle every step—so you don’t have to manage multiple suppliers.
We’ve helped clients across industries:
- An automotive parts maker switch from plastic to aluminum die-cast housings for better heat resistance.
- A consumer electronics brand reduce costs by 15% by optimizing their injection-molded housing design.
A medical device company launch a new product on time with our fast prototype-to-production workflow.
Final Checklist: Which Process Is Right for Your Housing Component?
Use this quick checklist to summarize your decision:
✅ If your housing needs: Metal, high strength/heat resistance, high volume (10k+ units) → Choose Die Casting.
✅ If your housing needs: Plastic, complex design, medium-to-high volume (5k+ units) → Choose Injection Molding.
✅ If you’re unsure: Contact Sunmy Hardware. Send us your drawings, samples, or project requirements, and our engineers will provide a free, no-obligation recommendation.
At Shenzhen Sunmy Hardware Co.,Ltd., we’re more than a manufacturer—we’re your partner in creating high-quality, custom housing components. Visit sunmyhardware.com to explore our case studies, view our production facilities, or request a quote. Let’s turn your design into a reality.
